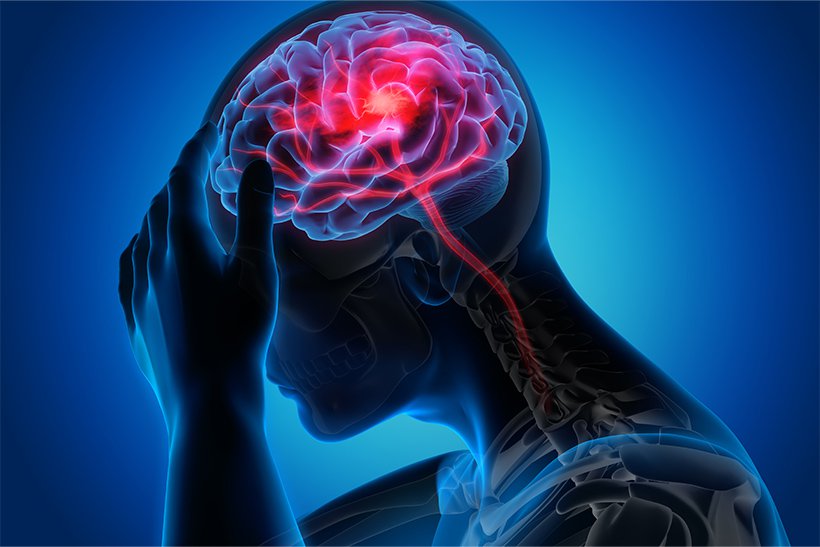
A stroke occurs when blood flow to part of the brain is blocked or a blood vessel bursts, causing brain cells to die. Recognizing the early signs of a stroke can save a life and prevent permanent brain damage. In this blog, we’ll explore the common symptoms, how to act fast, and the critical importance of early intervention.
What Is a Stroke?
A stroke is a medical emergency that happens when the brain’s blood supply is interrupted, either due to a blockage (ischemic stroke) or a ruptured blood vessel (hemorrhagic stroke). Without oxygen-rich blood, brain cells begin to due, leading to potential long-term disabilities or even death. The quicker you recognize the signs of a stroke and seek medical help, the better the chances of recovery.
The Most Common Signs of a Stroke
There are several early symptoms to look out for. Often, the most recognizable signs of a stroke include:
- Sudden Numbness or Weakness: This usually affects the face, arm, or leg, especially on one side of the body.
- Confusion: The person may suddenly have difficulty speaking or understanding what others are saying.
- Vision Problems: Blurred, double, or loss of vision in one or both eyes is a potential warning sign.
- Difficulty Walking: Sudden dizziness, loss of balance, or coordination could indicate a stroke.
- Severe Headache: A sudden, severe headache with no known cause could be a sign of a hemorrhagic stroke.
The FAST Method to Identify Signs of a Stroke
- F- Face Drooping: Is one side of the person’s face drooping or feel numb? Ask them to smile, and see if one side of their mouth is lower than the other.
- A- Arm Weakness: Ask the person to raise both arms. Does one arm drift downward or feel weak?
- S- Speech Difficulty: Is the person slurring their speech or having trouble finding words? Can they repeat a simple sentence clearly?
- T- Time to Call 911: If any of these symptoms are present, call emergency services immediately. Time is critical when dealing with a stroke.
Silent Strokes: A Hidden Danger
Not all strokes come with dramatic symptoms. Some strokes, known as “silent strokes”, have no obvious signs but still cause damage to the brain. These types of strokes may be detected later through brain scans and are often associated with memory loss, cognitive decline, and an increased risk of more severe strokes in the future.
Risk Factors for a Stroke
Several factors can increase the likelihood of experiencing a stroke. Some of the most common risk factors include:
- High Blood Pressure: The leading cause of a stroke, high blood pressure puts extra strain on blood vessels.
- Diabetes: People with diabetes have a higher risk of stroke due to blood vessel damage.
- Smoking: Smoking damages blood vessels and raises the risk of clot formation.
- Obesity: Being overweight increases the risk of high blood pressure and diabetes, both which are linked to strokes.
What to Do If You Suspect a Stroke
If you suspect someone is having a stroke, act immediately. Call 911 or your local emergency number. Even if the symptoms seem to disappear, the person still needs medical attention. Emergency treatments like clot-busting medications can significantly reduce the long-term effects of a stroke if administered within a few hours.
Conclusion: Time is Brain
Recognizing the signs of a stroke and acting fast can mean the difference between life and death. Always remember the FAST method to quickly assess the situation and seek immediate medical care. The quicker the treatment, the better the outcome for the individual. Don’t hesitate- time is brain.
American Online Benefits Group offer plans to support the medical needs and aftercare of a person who suffers a stroke. Contact our Member Services at (214) 389-9072 for more information.