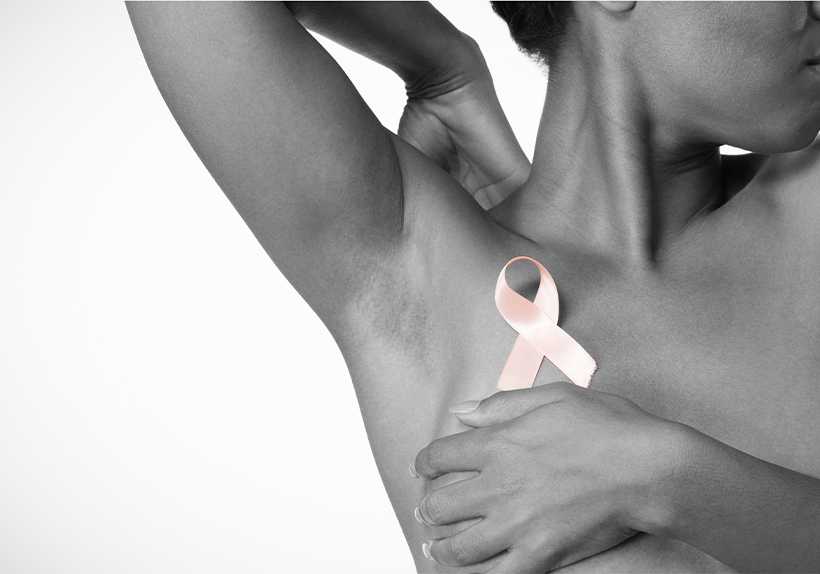
About 1 in 8 U.S. women (about 13%) will develop invasive breast cancer over the course of her lifetime.
Growth-Regulating Genes
Breast cancer is an uncontrolled growth of cancer cells due to mutations of growth-regulating genes. These genes control the growth and multiplication of cells; alterations in these genes result in cancerous changes. Breast cancer can occur in either lobules or ducts of the breasts.
Lobules are milk-producing cells while ducts are channels that guide the milk towards the nipples. The rest of the breast is filled with fatty tissues that can also undergo cancerous changes.
Usually, benign cancers are harmless and stay quite lifelong; malignant cancers are harmful that invade the normal tissues. Malignant breast cancers can spread to other parts of the body via lymph nodes.
Breast cancer became the most common cancer globally as of 2021, accounting for 12% of all new annual cancer cases worldwide, according to the World Health Organization.
Causes & Risk Factors
Rapid and continuous division of normal cells results in the accumulation of abnormal cells forming a breast lump. Cells may then metastasize to other parts.
Certain factors increase the chances of the occurrence of cancer. But remember that the presence of a few risk factors does not mean you will get breast cancer. The risk factors of breast cancers are following:
- Female gender (although breast cancer can occur in males as well)
- Old Age
- Race
- A family history of breast cancer
- Presence of abnormal genes
- Early menarche
- Late menopause
- Late pregnancy or no pregnancy
- Obesity or metabolic syndrome
- Alcoholism
- Taking hormone replacement therapy
Signs & Symptoms
Breast cancers usually start with swelling or a lump that may be too small to detect therefore, therefore may be asymptomatic in the early stages. One thing to note here is that not all breast lumps are cancerous.
The signs and symptoms of most breast cancers are following:
- Change in size and shape of the breast
- A breast lump that is increasing in size and adherent to underlying tissues
- Pain in the breast lump
- Redness and changes in skin texture of the involved breast
- Swelling in the breast
- Indrawing of nipples or inverted nipples
- No-milky nipple discharge
- Scaling or dimpling of the skin on the affected breast
Detection
If you develop an unusual breast lump your doctor will do a breast and general physical examination. In suspected cases the following diagnostic tests are done to rule out the symptoms:
Specific machines or gadgets are designed to maintain uninterrupted breathing. Examples are:
- Mammogram
- It’s a detailed X-ray of a breast
- Most common breast cancer screening method
- Annual mammography is recommended in women over 40 years of age
- Ultrasound
- It visualizes the deep breast tissues.
- It helps to differentiate between benign lumps and cysts
- MRI
- It is helpful in the advanced stages of breast cancer
During a biopsy, a doctor will remove small pieces from the suspicious area so they can be looked at in the lab to see if they contain cancer cells.
- A microscopic examination of breast tissue
- A biopsy will tell features of abnormal growth, grade, and abnormal genes
Breast cancer could be detected up to five years before there are any clinical signs of it, using a blood test that identifies the body’s immune response to substances produced by tumor cells, according to new research presented at the 2019 NCRI Cancer Conference.
- CBC
- Blood chemistry
Follow this link to learn more about self screenings: Breastcancer.org
Treatment
Early diagnosis and treatment are necessary to decrease the chances of recurrence and metastasis. The treatment of breast cancer depends on the stage, grade, and size of the tumor. Your doctor may choose the following treatment option depending on the stage and grade:
- Surgical Management
- Lumpectomy
- Lymph node removal surgery
- Mastectomy
- Radiotherapy
- Radiation from a source outside the body
- Placement of a radiation source inside the body.
- Chemotherapy
- Hormonal Therapy
- Medical Management
Surgery is useful in most cases as it removes the affected area and prevents the disease. Depending on the disease stage the following surgical options may be considered:
If breast cancer spreads to other parts of the body then radiation therapy is given after surgery. There are two types of radiotherapy:
Chemotherapy (chemo) uses anti-cancer drugs that may be given intravenously (injected into your vein) or by mouth. The drugs travel through the bloodstream to reach cancer cells in most parts of the body. Occasionally, chemo may be given directly into the spinal fluid which surrounds the brain and spinal cord.
Some types of breast cancer are affected by hormones, like estrogen and progesterone. The breast cancer cells have receptors (proteins) that attach to estrogen and progesterone, which helps them grow. Treatments that stop these hormones from attaching to these receptors are called hormone or endocrine therapy.
This is the all inclusive treatment of breast cancer. It can be the use of local treatments to remove cancer cells or make them smaller, or it can be a systemic treatment like chemotherapy and hormone therapy.
Prevention
Breast Cancers can be prevented by observing the following.
- Regular screening of breast cancer as advised by your physician
- Performing breast self-examinations
- Adopt a healthy lifestyle
- Stop alcohol intakeMaintain weight according to BMI
- Be sure to take healthy diets and avoid fast food or processed foods
- Prophylactic surgery in a very high-risk case as advised by your doctor
With breast cancer being a leading cause of death among the human race, there are also ways to detect this disease to increase your survival rate. At American Online Benefits Group, we offer products that provide our members with access to healthcare providers to maintain annual screenings. Contact our Agent or Member Services today for more information at 214-389-9072.